Procedures
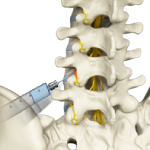
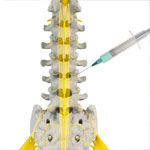
Facet Injections
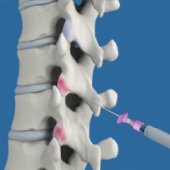
The facet joints are the tiny joints situated at the upper and lower part of each vertebra, connecting one vertebra to the other. Each vertebra has four facet joints: a pair that connects to the vertebra above (superior facets) and another pair that connects to the vertebra below (inferior facets). They guide motion and provide stability.
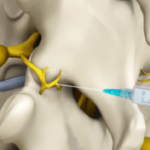
Medial Branch Block Injections
Medial Branch Block Injections is a painful condition caused by the irritation of the sciatic nerve. Medial Branch Block Injections can be acute (short term), lasting for a few weeks or chronic (long term), persisting for more than 3 months. It is important to understand that in most cases, Medial Branch Block Injections will resolve itself within a few weeks or months and rarely causes permanent nerve damage.
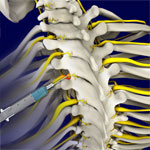
In-Office Cervical Injections
In-office cervical injections are administered in a medical office or clinic setting to provide relief from pain or inflammation affecting the neck and upper back. The injection is made in the patient’s epidural space, which is the area between the outermost covering of the spinal cord, the dura mater, and the wall of the spinal canal.
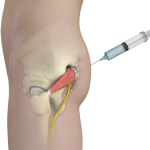
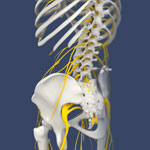
Piriformis Muscle Injection
The piriformis muscle is present in the buttocks, connecting the sacrum to the outer surface of the hip. This muscle enables us to walk and run. The sciatic nerve is a thick, long nerve passing through or below the piriformis muscle.
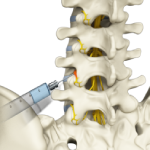
In-Office Lumbar Injections
In-office lumbar injections are steroid shots administered to you in your physician’s clinical or office setting to relieve low back pain. These shots involve injecting a local anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory steroid into the lumbar (lower back) area of your spine. Your doctor decides on the appropriate injection depending on the source of the pain in your lumbar area.
Transforaminal Epidural Block
An epidural block or epidural spinal injection is a non-surgical treatment option for relieving back pain and other symptoms.Epidural blocks contain a strong anti-inflammatory agent called corticosteroid and an anesthetic for pain relief.
Lumbar Epidurals
Lumbar epidurals are injections to treat and relieve low back pain. A lumbar epidural involves injecting a local anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory steroid into the epidural space of the lower spine (lower back) to reduce inflammation causing the pain.
Thoracic Facet Joint Injection
Facet joints are small joints present between the vertebral bones including the vertebral bones of the thorax (upper back). The bones in these joints are covered by cartilage and a capsule filled with synovial fluid surrounds the joint reducing friction. Thoracic facet joints can be affected by injury, mechanical stress or arthritis causing pain in the mid-back, chest and rarely the arms.
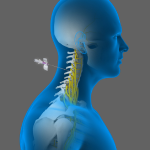
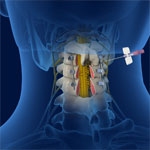
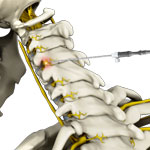
Cervical Epidurals
A cervical epidural is an injection of medication into the epidural space in the lower section of the cervical region to provide relief from pain or inflammation affecting the neck and upper back. The epidural space is the space between the outermost covering of the spinal cord (dura mater) and the wall of the spinal canal and runs along the length of your spinal cord. It is approximately 5 mm wide and is filled with spinal nerve roots, fat, and blood vessels.
Cervical & Lumbar Injections
Cervical injections are administered in a medical office or clinic setting to provide relief from pain or inflammation affecting the neck and upper back. The injection is made in the patient’s epidural space, which is the area between the outermost covering of the spinal cord, the dura mater, and the wall of the spinal canal. It runs along the length of your spinal cord, is approximately 5 mm wide and is filled with spinal nerve roots, fat, and blood vessels.
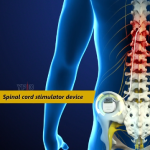
Spinal Cord Stimulator
A spinal cord stimulator is a device that sends electrical impulses to the areas of the spinal cord causing pain and interferes with the transmission of pain signals to the brain. It blocks the brain's ability to sense pain in the stimulated areas, thus relieving pain without the side effects that medications can cause. The electrical impulses can be targeted to specific locations and, as pain changes or improve, stimulation can be adjusted as necessary.
Hardware Blocks
A hardware block is a minimally-invasive method to diagnose and treat chronic pain, especially for people who have undergone a spinal fusion surgery in the past and are suspected to have pain due to the hardware inserted from the previous surgery.
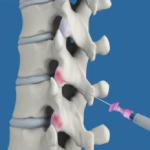
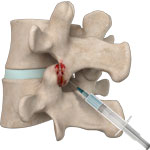
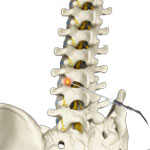
Lumbar Facet Block
A facet block is a procedure in which a combination of a local anaesthetic and a corticosteroid is injected into a facet joint. A lumbar facet block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the lower back.
Lumbar Medial Branch Block
A medial branch block is a procedure in which a mixture of a local anaesthetic with or without a corticosteroid is injected near the medial branch nerves supplying a facet joint. A lumbar medial branch block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the lower back.
Lumbar Sympathetic Block
Sympathetic nerves located in the lower spine control basic functions such as regulating blood flow. They also carry pain signals from tissues to the spinal cord.
Lumbar Spondylosis Radiofrequency Ablation
Coming soon
Cervical Facet Radiofrequency Neurotomy
Coming soon
Selective Nerve Root Block
A selective nerve root block is the injection of an anaesthetic and steroid medication around the spinal nerve root to diagnose or treat pain. It is indicated to relieve pain, weakness, numbness and tingling sensation in your neck, back and extremities due to nerve injuries such as a pinched nerve and spinal stenosis (narrowing).